See a Doctor
Within Minutes
Skip the unnecessary waiting room,
see a board-certified clinician now.
Available in 50 states. No insurance needed.
AS SEEN IN

Prescriptions as needed
Renew or get a new Rx.
On-demand virtual visits
See a physician 24/7.
24/7 care support
We are here to help you.

World-class care team
- All of our clinicians are board-certified and trained in the top U.S. medical schools.
- Our providers are qualified to diagnose and treat a wide variety of non-emergency conditions.
- We approach patient care with the best clinical practices to provide personalized treatment.
Comprehensive care, where you are

Virtual Urgent Care
On-demand board-certified clinicians ready to take care of your virtual urgent care needs.
Men's Health
Thorough on-demand care by a medical professional for all your men’s health concerns.
Women’s Health
Your urgent women’s health concerns handled personally by a board-certified clinician.
Virtual Primary Care
Get expert advice and a treatment plan from DrHouse virtual primary care providers.
Online Prescriptions
Get treatment and expert advice from DrHouse online doctors.

Online Dermatology
Get treatment and expert advice for thousands of skin conditions.
Online Gynecology
Get expert advice, a treatment plan, and an Rx from DrHouse online doctors.

Online Doctor
Get expert advice, a treatment plan and prescriptions from online doctors.
Doctor’s Note
Get a Doctor's Note for School or Work
Telehealth Services
Discover all of our telehealth services, designed to meet all of your healthcare needs.
Comprehensive care, where you are
-
Virtual Urgent CareTreatment Prescriptions
-
Men's HealthTreatment Prescriptions
-
Women’s HealthTreatment Prescriptions
-
Virtual Primary CareTreatment Prescriptions
-
Online PrescriptionsTreatment Prescriptions
-
Online DermatologyTreatment Prescriptions
-
Online GynecologyTreatment Prescriptions
-
Online DoctorTreatment Prescriptions
-
Doctor’s NoteTreatment Prescriptions
-
Telehealth ServicesTreatment Prescriptions
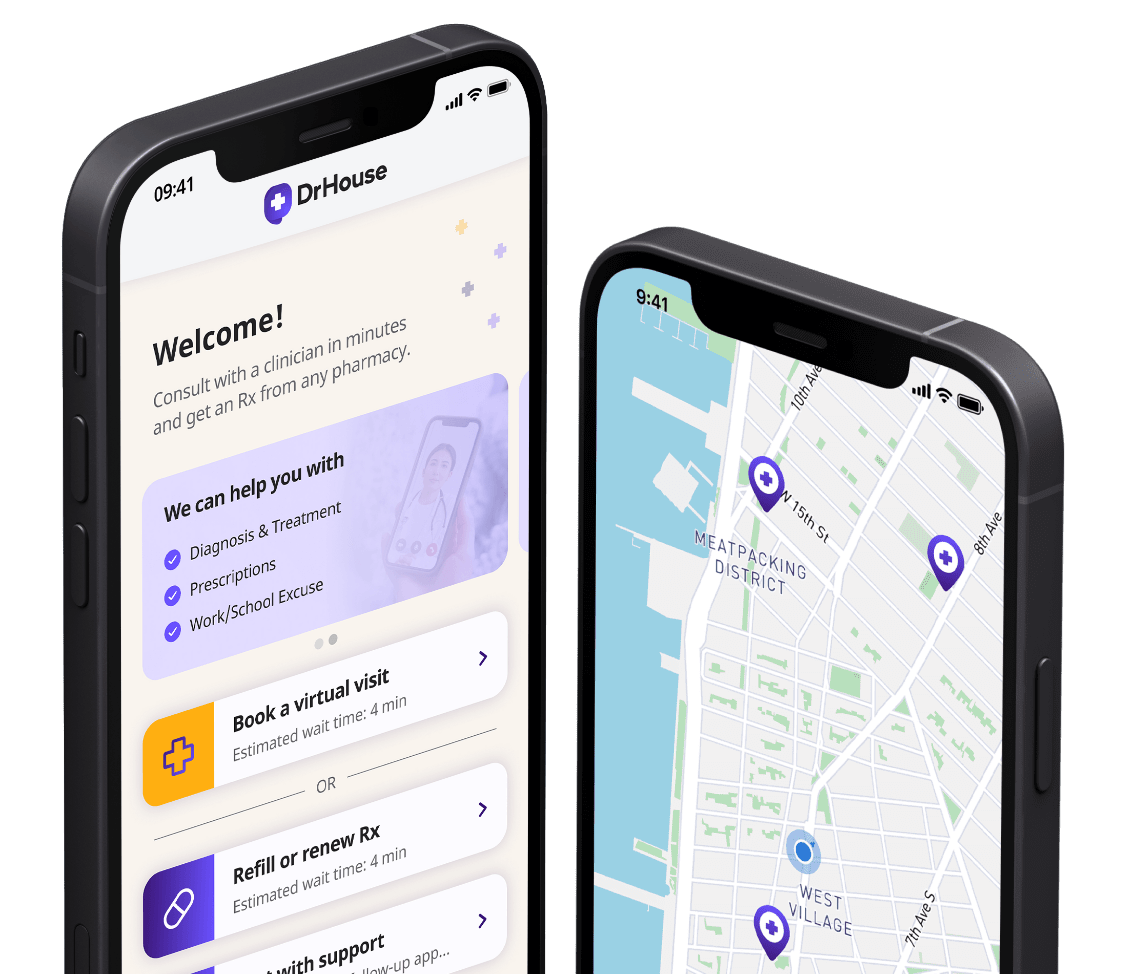
Download our app
See why people turn to DrHouse...
Lifesaver
I’m so grateful that I found this app. I know they have a launch special right now and all visits are free, but what an amazing...
Jessica E.
AMAZING!!
It was a great overall experience! It literally took me less than 5 minutes to speak with a doctor!
Emma D.
First time user
Doctor was very attentive and listened to what I told her. I hope they will start delivering medications soon...
Anonymous
Definitely using...
I appreciate the doctor and the excellent care she provided me. I would recommend her and this service without hesitation.
Anonymous
Good start
I have had 2 visits so far for my chronic condition, you can’t get same doctor but overall it's great!
Lando M.
Got my prescript...
It was a very positive experience. Wait time was less than 5 minutes and got my prescription in 15 minutes!
Harry C.
Not bad at all
My doctor was firendly and listened to me. I probably saved couple of hours and never had to leave my home.
Ava E.
Best healthcare a...
My new favourite healthcare app on the go. One of the easiest and most convenient services out there.
Anonymous
Convenient
My call with the doctor took less than 15 minutes. It saved me an urgent care visit and quite a lot of money.
Matt T.
Learn more about healthcare
Is Vancomycin a Broad-Spectrum Antibiotic?
Vancomycin is an antibiotic prescribed to treat bacterial infections, and because of its activity in cases of drug resistance, it is often reserved for serious infections. However, is vancomycin considered a broad-spectrum antibiotic? Although it only treats infections from gram-positive bacteria, Vancomycin is considered broad-spectrum. This is because it still treats a range of infections… Continue reading Is Vancomycin a Broad-Spectrum Antibiotic?
Jessica Guht Dec. 11, 2023
Essential Oils for UTIs: Can They Help Treat a UTI?
Jessica Guht Dec. 04, 2023
